What is Catalytic Converter?
A catalytic converter is a crucial emissions control device in the exhaust system of a vehicle, such as a car or truck. Its primary function is to reduce harmful pollutants produced during the combustion process in the engine and convert them into less harmful gases.
How a Catalytic Converter Works?
- Pollution Reduction: When your vehicle’s engine burns fuel (gasoline or diesel), it produces exhaust gases that contain harmful pollutants, particularly carbon monoxide (CO), unburned hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
- Catalyst:
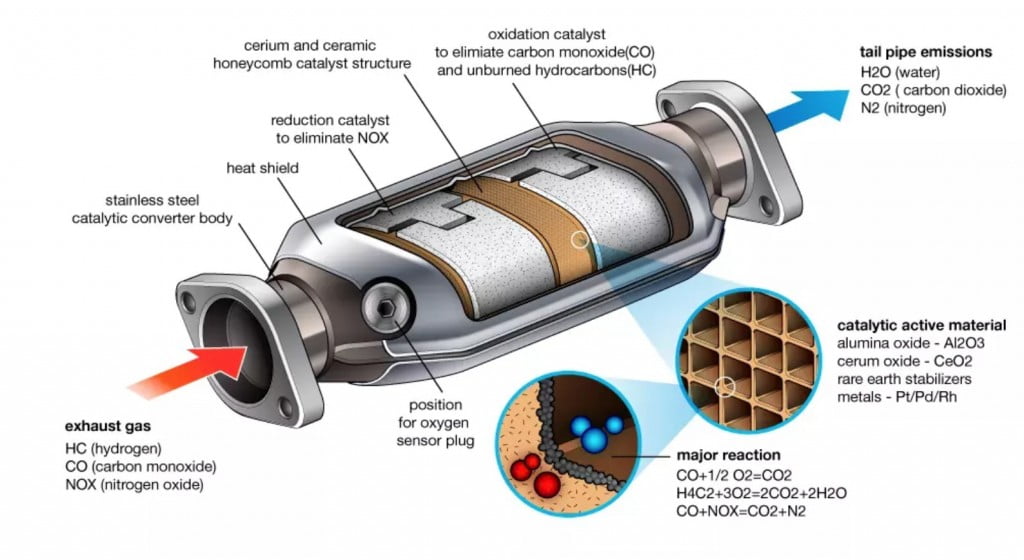
- Inside the catalytic converter, there are catalysts, typically made of precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These catalysts are coated on a ceramic or metallic honeycomb structure.
- As the exhaust gases flow through the catalytic converter, the catalysts facilitate chemical reactions that transform the harmful pollutants into less harmful substances.
- Chemical Reactions:
- Carbon monoxide (CO) is converted into carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Unburned hydrocarbons (HC) are oxidized into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are reduced to nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2).
- Cleaner Exhaust: The end result is cleaner exhaust that contains fewer harmful pollutants, which is released into the environment.
CarBlogIndia
Why Catalytic Converters Are Important?
Catalytic converters play a critical role in reducing air pollution and improving air quality. They are essential for the following reasons:
- Environmental Protection: Catalytic converters help reduce the emission of harmful pollutants that contribute to smog, acid rain, and poor air quality. This is especially important in urban areas with high vehicle traffic.
- Compliance with Emission Standards: Many countries and regions have stringent emission standards that require vehicles to have catalytic converters to meet these standards and reduce their environmental impact.
- Health Benefits: By reducing pollutants, catalytic converters help minimize the health risks associated with breathing in toxic exhaust fumes, which can cause respiratory problems and other health issues.
- Fuel Efficiency: Catalytic converters can also contribute to better fuel efficiency by improving the combustion process and reducing wasted fuel.
CalMatters
What cars have Catalytic Converters?
Catalytic converters are a standard component in the exhaust systems of most modern gasoline and diesel-powered vehicles. This includes a wide range of cars, trucks, and other motor vehicles produced in compliance with emissions regulations. While the specifics can vary by make and model, virtually all vehicles produced since the 1980s are equipped with catalytic converters.
This includes vehicles from various manufacturers such as:
- Toyota
- Ford
- Chevrolet (Chevy)
- Honda
- Volkswagen (VW)
- Nissan
- Hyundai
- BMW
- Mercedes-Benz
- Audi
- Jeep
- Subaru
- Kia
- Mazda
- Chrysler
- Lexus
- Volvo
- Tesla (for electric vehicles with range extenders)
Catalytic converters are a crucial component for reducing harmful emissions and are required by emissions regulations in most countries to help mitigate the environmental impact of vehicle emissions. Vehicles with non-compliant or tampered catalytic converters may not meet legal emissions standards and could face penalties, fines, or restrictions.
It’s important to maintain and ensure the proper functioning of the catalytic converter in your vehicle to comply with emissions regulations and reduce environmental impact.
Lake region
Do electric cars have catalytic converters?
Electric cars, which are powered by electric motors and use electricity as their primary energy source, do not have traditional catalytic converters like those found in gasoline or diesel-powered vehicles.
The reason for this is that electric vehicles (EVs) produce zero tailpipe emissions of harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) during operation. Instead, EVs rely on batteries to store and deliver electrical energy to power the vehicle.
Since catalytic converters are designed to reduce emissions from internal combustion engines, which burn fossil fuels and produce exhaust gases with harmful pollutants, they are not needed in electric cars. The absence of a combustion engine and exhaust system in EVs means there are no tailpipe emissions to control or reduce.
Electric cars are considered a cleaner and more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, as they help reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. However, it’s important to note that the overall environmental impact of an electric vehicle, including the production and disposal of batteries and the source of the electricity used for charging, can still have environmental considerations.
Animagraffs
READ ALSO: Tesla bike rack: 3 Best options for Model 3
FAQs
Is there a catalytic converter in a Tesla?
Tesla electric vehicles (EVs), such as the Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y, do not have traditional catalytic converters like those found in internal combustion engine vehicles (gasoline or diesel-powered vehicles). Since Teslas operate entirely on electric power and do not have internal combustion engines, they produce no tailpipe emissions of harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
Catalytic converters are designed to reduce emissions from internal combustion engines by converting harmful exhaust gases into less harmful substances. Since Tesla EVs do not have exhaust systems and do not generate such emissions, catalytic converters are not a necessary component of their design.
While Tesla vehicles do not have catalytic converters, they contribute to environmental benefits by producing zero tailpipe emissions. The environmental impact of an electric vehicle like a Tesla is primarily associated with the source of the electricity used for charging and the production and disposal of the vehicle’s batteries. In many cases, the use of renewable energy sources for charging can further reduce the environmental footprint of electric vehicles.
REREV
Do hybrid cars have catalytic converters?
Yes, hybrid cars, which combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor and battery, typically have catalytic converters.
The presence of a catalytic converter in hybrid vehicles is primarily related to the fact that they include a gasoline or diesel engine, which generates exhaust emissions that require treatment to reduce harmful pollutants.
Catalytic converters in hybrid vehicles serve the same purpose as in traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, which is to reduce harmful emissions from the combustion process. The catalytic converter in a hybrid car helps convert pollutants like carbon monoxide (CO), unburned hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into less harmful substances.
While hybrid vehicles have the advantage of electric power for low-speed and stop-and-go driving, they also have an internal combustion engine that operates under certain conditions, such as when the battery is depleted or additional power is needed. As a result, the catalytic converter is an important emissions control component in hybrid vehicles, helping to meet emissions standards and reduce environmental impact.
Are catalytic converters only on petrol cars?
Catalytic converters are not exclusive to petrol (gasoline) cars; they are also present in diesel-powered vehicles. In fact, catalytic converters are commonly found in the exhaust systems of both gasoline and diesel internal combustion engine vehicles.
Catalytic converters serve the same essential function in both types of vehicles, which is to reduce harmful emissions produced during the combustion process. These emissions include pollutants like carbon monoxide (CO), unburned hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). The catalytic converter’s role is to facilitate chemical reactions that convert these harmful gases into less harmful or inert substances, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and nitrogen (N2).
To meet emissions regulations and reduce the environmental impact of vehicle exhaust, both gasoline and diesel vehicles are equipped with catalytic converters. The design and operation of the catalytic converter can differ slightly between gasoline and diesel vehicles due to variations in the types of emissions and combustion processes associated with each fuel, but the core function remains the same.
Why are catalytic converters often stolen?
Catalytic converter theft has become a significant issue in many regions, and several factors contribute to why catalytic converters are often stolen:
- Precious Metals: Catalytic converters contain valuable precious metals, such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium, which are used as catalysts to facilitate chemical reactions that reduce harmful emissions. These metals have high market value, making catalytic converters an attractive target for thieves.
- Ease of Theft: Catalytic converters are relatively accessible and can be removed with basic tools, such as a reciprocating saw or wrench, making them a quick and easy target for thieves.
- Lack of Serial Numbers: Unlike many car parts, catalytic converters generally lack unique serial numbers or identifying markings, which makes it difficult to trace stolen converters back to their original vehicles.
- Reduced Risks for Thieves: Stealing catalytic converters can be a low-risk crime for thieves, as they can be in and out quickly without drawing much attention.
- High Replacement Costs: When a catalytic converter is stolen, the vehicle owner faces a substantial replacement cost, which can be several hundred to over a thousand dollars, depending on the vehicle make and model.
- Limited Regulation: There may be limited regulation and oversight of scrap metal buyers, making it easier for thieves to sell stolen catalytic converters.
- Recycling Industry: The valuable metals inside catalytic converters are in demand in the recycling industry, where they can be processed and resold.
To prevent catalytic converter theft, some vehicle owners take measures like installing anti-theft devices, etching serial numbers on the converter, or parking in well-lit areas. Additionally, law enforcement agencies and local governments have been working to combat this type of theft by implementing regulations and cracking down on the sale of stolen converters in the recycling industry.